5 Types of Renewable Energy
Renewable Energy is becoming more critical than ever. As climate change worsens and fossil fuels run out, we need renewable Energy solutions. Options like solar and wind power help reduce pollution and ensure we have affordable and clean energy for the future.
What is Renewable Energy?
Sustainable energy comes from natural processes that are constantly replenished. Unlike coal, oil, and gas, it’s environmentally friendly and has a much smaller ecological impact.
Key Points:
- It uses sources like sunlight, wind, water, and organic materials.
- It’s sustainable for future generations.
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy:
- Renewable Sources: Come from endless sources like the sun and wind.
- Non-Renewable Sources: Rely on finite resources like coal and oil, which pollute the environment.
Why is Clean Energy Important?
Environmental Benefits:
- Cuts greenhouse gas emissions, reducing global warming.
- Lowers air and water pollution, protecting nature.
Economic Advantages:
- Creates jobs in green industries.
- Reduces dependence on imported fuels, boosting energy security.
Social and Health Benefits:
- Improves public health by cutting pollution-related diseases.
- Provides power to remote areas, improving quality of life.
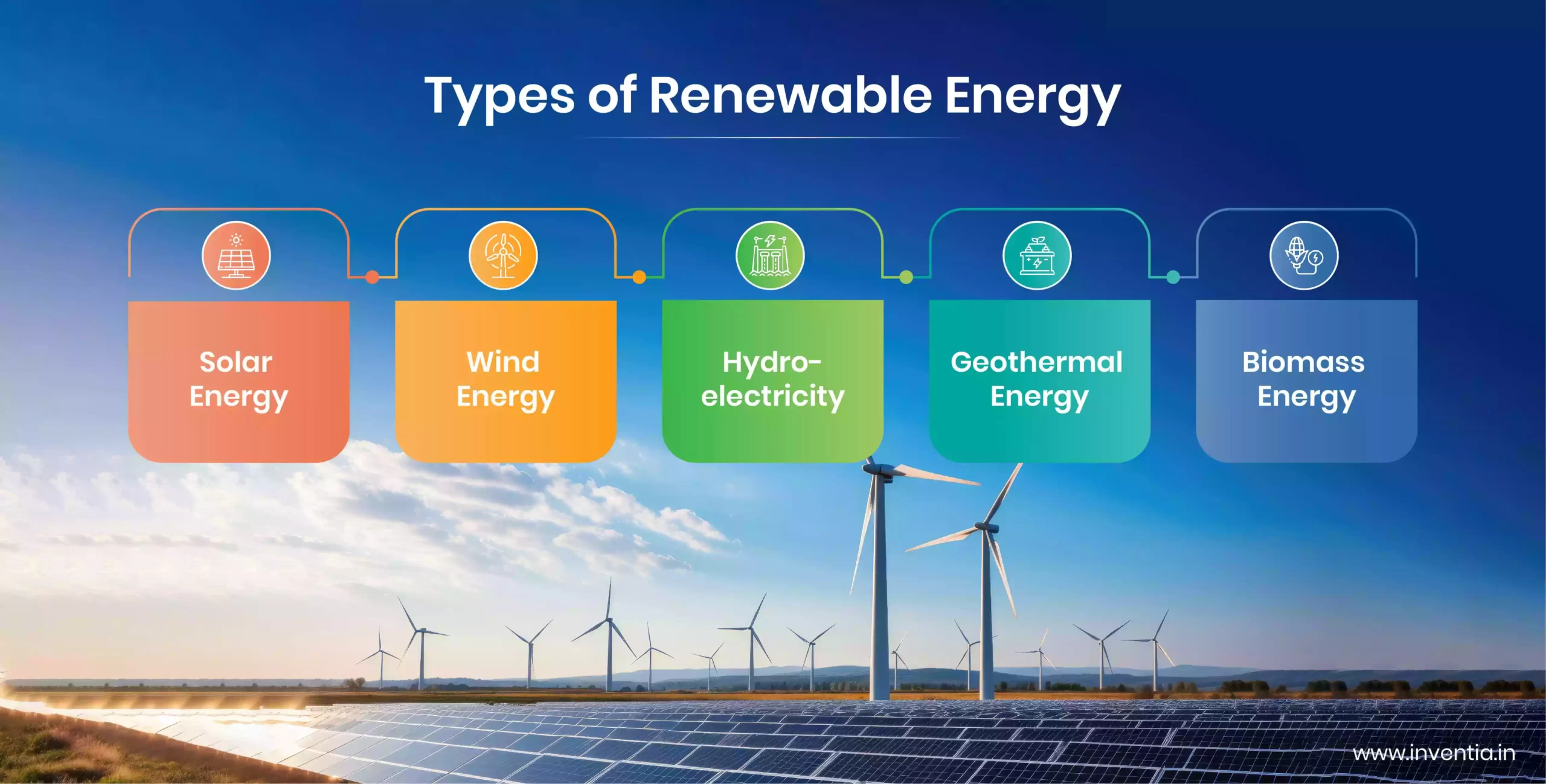
Types of Renewable Energy

1. Solar Power
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun to produce electricity or heat. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, while solar thermal systems focus sunlight to generate heat for industrial processes or water heating. Solar energy is versatile, powering everything from homes and businesses to entire solar farms that feed into the grid.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy uses turbines to capture the kinetic energy of moving air and convert it into electricity. Onshore wind farms are common in open areas with steady winds, while offshore wind farms leverage stronger, more consistent sea breezes. Wind energy is one of the fastest-growing clean energy sources, contributing significantly to global energy needs.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower generates electricity by using the flow of water to turn turbines. Dams are the most common way to harness this energy, but river-based systems and tidal power are also growing in popularity. Hydropower is reliable and can quickly scale up or down to meet electricity demands, making it a crucial part of many energy systems.
4. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat, found below the surface. This heat can be used directly for heating buildings or generating electricity through steam-driven turbines. Geothermal plants operate continuously, providing a stable and eco-friendly energy source with minimal environmental impact.
5. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from organic materials such as plants, agricultural waste, and wood. These materials are burned or processed to produce heat, electricity, or biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. Biomass helps recycle waste products, reducing landfill use and providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
How Renewable Energy Works
Each type of clean energy works differently but achieves the same goal: converting natural resources into power.
- Solar: Sunlight becomes electricity through solar panels.
- Wind: Wind spins turbines to generate power.
- Hydropower: Flowing water turns turbines to create electricity.
- Geothermal: Heat from the Earth produces steam for turbines or provides direct heating.
- Biomass: Organic materials are burned or processed to release energy.
Examples include powering homes, running businesses, and fueling transportation.
Government policies
India’s renewable energy policies focus on reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting sustainable energy development. With ambitious targets like 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030, initiatives such as the National Solar Mission and KUSUM scheme support solar, wind, and biomass energy projects. These efforts align with international commitments like the Paris Agreement to ensure a greener, more sustainable future.
Current Trends and Innovations in Green Energy
Emerging Technologies:
- Floating solar farms use less land.
- Better batteries store more energy for later use.
Success Stories:
- Denmark leads in wind energy.
- India has built massive solar parks, including the world’s largest.
Challenges and Solutions
Infrastructure and Storage:
- Problem: Limited capacity for storing energy.
- Solution: Develop better batteries and storage systems.
Public Awareness:
- Problem: Misinformation slows adoption.
- Solution: Educate people and offer incentives for going green.
How You Can Support Renewable Energy
Personal Actions:
- Install solar panels or choose green energy providers.
- Save energy by using efficient appliances.
Advocating for Change:
- Support policies that promote sustainable energy.
- Push local governments to fund green projects.
Investing in Green Projects:
- Invest in stocks or community programs focused on clean energy.
- Participate in energy certification programs.
The Future of Renewable Energy
The future of clean energy is bright. By 2030, solar and wind could dominate electricity generation. By 2050, we might rely almost entirely on sustainable power. Achieving this requires effort from everyone — individuals, businesses, and governments.
By choosing sustainable energy and alternative energy sources, we can create a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations.

